Please note
Arada no longer manufactures boiler stoves at present. The information on this page has been provided for the benefit of existing Ecoboiler stove owners only.
- Documentation for discontinued Ecoboiler stoves can be found in our Ecoboiler stove information archive.
- Documentation for older discontinued Stratford boiler stoves can be found in our Stratford boiler stove information archive.
Guide to Choosing a boiler stove
When calculating your boiler stove requirements please allow, as a guide, 1kW per square metre of single panel radiator (multiply up if double or triple panelled radiator).
If domestic hot water is being heated then also add the kW requirement for the cylinder/thermal store (approx 3kW to heat a 120l cylinder for example).
Heat loss throughout the system needs to be factored in. This is usually around 10% for modern plumbing systems but can increase/decrease depending on pipework being lagged etc.
The information above acts as a general guideline only. We highly recommend that you contact a qualified heating engineer who will ensure that you make the right choice for your home.
Output to water
The Output to Room (kW) is quoted for our boiler stoves as a guide only and a correctly sized and installed stove will in general provide very little heat to the room. The Output to Water (kW) value indicates the typical heat output to hot water and radiators.
The boiler can be configured as a fully pumped system for radiators only but will still require the header tank and open vent together with a heat leak radiator. The stove does not need to be installed to a hot water tank BUT still must be fitted to a gravity circuit with at least 3 pipes connected to the stove (See page 20 & 22 of wet install guide)
The boiler stove is not recommended for a purely hot water-only application as it may be oversized and therefore may run at inefficient burn rates for most of the time. Once the cylinder water temperature demand has been satisfied, the boiler would close down for long periods causing possible tarring problems, particularly if wood is the primary fuel.
A typical boiler stove installation
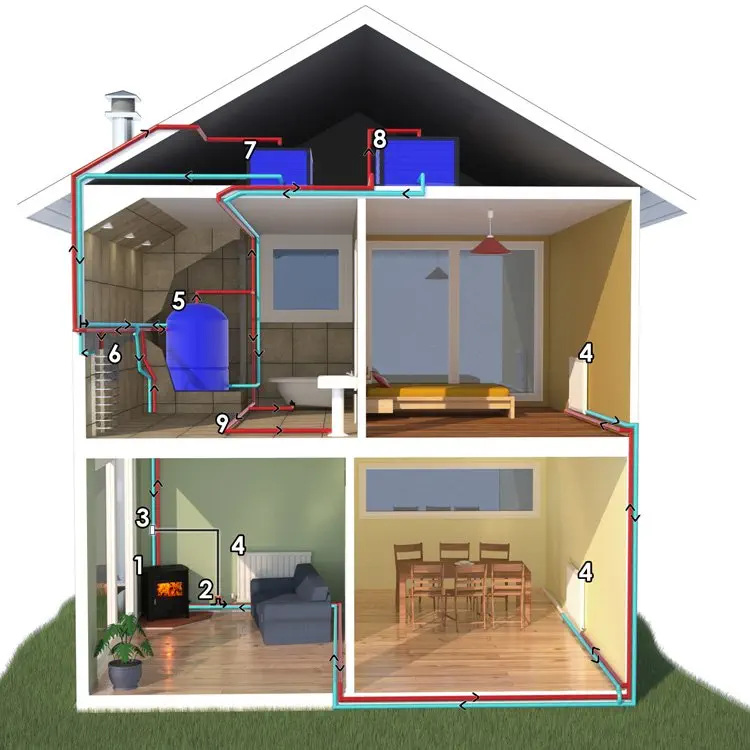
| 1 | Boiler Stove | 2 | Circulating Pump | 3 | Pipe Thermostat |
| 4 | Radiators | 5 | Indirect Hot Water Tank | 6 | Gravity Radiator |
| 7 | Feed & Expansion Tank | 7 | Cold Water Tank | 9 | Domestic Hot Water |
Connecting a boiler stove with oil or gas boilers
It is possible to use an Arada boiler in conjunction with a pressurised gas or oil boiler as part of a larger system perhaps including Solar or Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP). However, this can only be done with the use of a Thermal Store or neutraliser, which will effectively isolate the boiler stove from the other components in the system and provide all the necessary safety elements.
There are many companies offering suitable thermal store systems. Arada cannot recommend any specific models or manufacturers of thermal stores. Your installer should be best placed to advise on a suitable model for the intended installation and system.
Hot water circuit
The hot water element of the output is installed as a thermosiphon and is often called a gravity circuit. This is connected with large bore pipe work, usually 28mm diameter but it can be larger. The water on the output side of the stove is much hotter than the input side and therefore less dense. This causes the heavier cold water to pull the hot water up and through the hot water cylinder coil. Essential solid fuel central heating system components such as the heat leak radiator, header tank and open vent should be installed on the output side.
The gravity circulation relies on a very small amount of energy to drive it and is therefore easily restricted or stopped.
To ensure a reliable gravity circulation circuit it is important to confirm:
- Large bore pipe work (28mm minimum)
- No valves or restriction in the pipe work or heat leak radiator
- Continuously rising pipes on the hot side, never falling
- Short run pipes. Ideally no more than 6m and directly above the stove for the best flow rate
- The cylinder must be higher than the stove outlet - the higher the better.
Radiator Output Circuit
There are a number of common configurations for the radiator side of the boiler output, varying in complexity according to specific installation needs. Some schematic diagrams of typical installations can be seen in the boiler stove product manual.
Additional methods, not described in the manual, call for the use of a Thermal Store or Neutraliser Tank.
The radiator circuit will be pumped and uses different terminals to those used for the hot water gravity circuit. The best installation method can only be determined by a site visit from a suitably qualified engineer as part of a competent person's scheme.
Pressurised Systems
A pressurised system has a normal operation pressure above that of a normal vented system with an atmospheric pressure vent pipe (approximately 1 bar in a typical installation).
Only our Ecoboiler Wood 12 stove can be used in a pressurised system as it has the mandatory safety features incorporated (quench coil loop and TAS valve connection point). It is unsafe to operate the rest of our Ecoboiler range of stoves in a pressurised system and constitutes a serious hazard to do so.
Open Vented System
An open vented system is a wet heating system incorporating a header tank fill system and an atmospheric pressure level vent, (normally vented back into the header tank, or outside the building).
With the exception of the Ecoboiler Wood 12 boiler stove that has been fitted with the quench coil and TAS valve for cold main water, all add-in and integral Arada boilers must be installed in an open vented system.
